Emergency medical services (EMS) stand as the frontline warriors in healthcare, providing critical care to those in life-threatening situations. From responding to accidents and medical emergencies to coordinating disaster relief efforts, EMS personnel play a pivotal role in ensuring the health and safety of our communities.
The EMS system encompasses a complex network of components, including dispatch centers, ambulances, paramedics, and emergency physicians. Each component works seamlessly to provide timely and effective medical care to patients in need. EMS personnel undergo rigorous training and certification to ensure they possess the skills and knowledge to handle a wide range of medical emergencies.
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Overview

Emergency Medical Services (EMS) is a comprehensive system that provides emergency medical care to individuals in need. EMS encompasses a wide range of services, including pre-hospital care, transportation, and hospital care. The primary goal of EMS is to provide timely and effective medical attention to patients experiencing acute illness or injury.
Role of EMS in the Healthcare System
EMS plays a crucial role in the healthcare system by providing immediate medical assistance to patients in emergency situations. EMS professionals are trained to assess patients’ conditions, provide life-saving interventions, and transport them to appropriate medical facilities. By providing timely and efficient care, EMS helps to improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality rates.
Examples of EMS Services
EMS services include a wide range of medical interventions, including:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Defibrillation
- Intubation
- Trauma care
- Patient transportation
li>Medication administration
EMS System Components
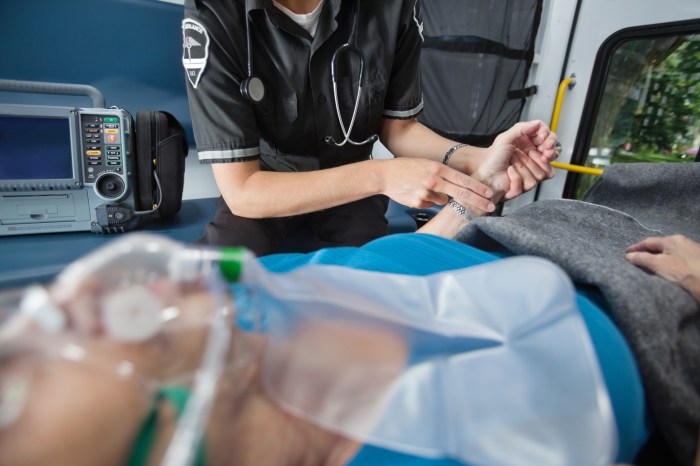
An Emergency Medical Services (EMS) system is a coordinated network of personnel, equipment, and facilities that provide emergency medical care to patients in need. The system is typically divided into four main components: dispatch, response, transport, and medical care.The dispatch component is responsible for receiving emergency calls and dispatching the appropriate EMS resources to the scene.
The dispatcher will gather information about the patient’s condition, location, and any other relevant details. The dispatcher will then dispatch the closest and most appropriate EMS unit to the scene.The response component is responsible for responding to emergency calls and providing initial medical care to patients.
The response unit will typically consist of two or more EMS personnel, who will arrive on scene in an ambulance or other emergency vehicle. The EMS personnel will assess the patient’s condition, provide basic life support, and transport the patient to the nearest hospital or emergency department.The transport component is responsible for transporting patients from the scene of an emergency to a hospital or emergency department.
The transport unit will typically consist of an ambulance or other emergency vehicle that is equipped with the necessary medical equipment to provide ongoing care to the patient during transport.The medical care component is responsible for providing medical care to patients at the hospital or emergency department.
The medical care team will typically consist of physicians, nurses, and other medical personnel who will assess the patient’s condition, provide treatment, and monitor the patient’s progress.
EMS Personnel
EMS personnel are the backbone of the EMS system. They are responsible for providing emergency medical care to patients in need, and they must be trained and qualified to perform their duties effectively.EMS personnel typically have a minimum of an EMT-Basic certification, which requires at least 120 hours of training.
EMT-Basics are trained to provide basic life support, including CPR, first aid, and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).Some EMS personnel also have advanced training, such as EMT-Intermediate or Paramedic certification. EMT-Intermediates are trained to provide more advanced life support, including the administration of certain medications and the use of advanced airway management techniques.
Paramedics are the most highly trained EMS personnel, and they are able to provide a wide range of advanced life support services, including the administration of medications, the use of advanced airway management techniques, and the performance of certain medical procedures.
Coordination and Communication
Coordination and communication are essential for the effective operation of an EMS system. The different components of the system must be able to work together seamlessly to ensure that patients receive the care they need in a timely manner.Communication between the different components of the EMS system is typically accomplished through the use of a centralized dispatch system.
The dispatch system allows the dispatcher to receive emergency calls, dispatch EMS resources to the scene, and track the status of EMS units in the field.The use of a centralized dispatch system helps to ensure that EMS resources are dispatched to the scene in a timely manner and that patients receive the care they need as quickly as possible.
EMS Operations
EMS operations encompass the core activities and procedures involved in providing emergency medical care to patients in need. These operations typically follow a standardized workflow to ensure efficient and effective response.
Workflow of EMS Operations
The typical workflow of EMS operations involves several key steps:
Dispatch
Upon receiving an emergency call, dispatchers gather information about the incident and patient’s condition. They then dispatch the appropriate EMS units to the scene.
Arrival and Assessment
EMS personnel arrive at the scene and conduct a rapid assessment of the patient’s condition. This includes checking vital signs, assessing injuries, and gathering information from witnesses or bystanders.
Stabilization and Treatment
Based on the assessment, EMS personnel provide immediate stabilization and treatment to the patient. This may involve administering medications, splinting injuries, or performing other life-saving interventions.
Transportation
If necessary, the patient is transported to a hospital or other medical facility for further care. During transport, EMS personnel continue to monitor the patient’s condition and provide ongoing treatment.
Documentation and Reporting
After the patient is transferred to the hospital, EMS personnel document their findings and complete a report of the incident. This information is used for billing, quality assurance, and research purposes.
Use of Medical Equipment and Protocols
EMS personnel use a variety of medical equipment and protocols to provide care to patients. These include:
Vital Signs Monitors
These devices measure and display the patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
Oxygen Tanks and Masks
Oxygen is administered to patients who have difficulty breathing or who have suffered a cardiac arrest.
Intubation Equipment
This equipment is used to insert a breathing tube into the patient’s airway to ensure adequate ventilation.
Defibrillators
These devices deliver an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal heart rhythm in patients who are experiencing cardiac arrest.
Medications
EMS personnel are trained to administer a variety of medications, including pain relievers, anti-nausea drugs, and cardiac medications.
Protocols
EMS personnel follow established protocols for assessing and treating patients. These protocols are based on evidence-based practices and are designed to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
Challenges and Risks Faced by EMS Personnel
EMS personnel face a number of challenges and risks in the course of their work. These include:
Physical and Emotional Stress
EMS personnel often work in high-stress environments and may be exposed to traumatic events. This can lead to physical and emotional exhaustion.
Exposure to Infectious Diseases
EMS personnel are at risk of exposure to infectious diseases, such as HIV, hepatitis, and tuberculosis.
Workplace Violence
EMS personnel may be at risk of workplace violence, such as assaults or verbal abuse.
Long Hours and Irregular Schedules
EMS personnel often work long hours and irregular schedules, which can disrupt their personal lives.
Burnout
EMS personnel may experience burnout due to the demanding nature of their work.
EMS Training and Education
EMS personnel undergo comprehensive training and education to equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide emergency medical care. Ongoing professional development is crucial to maintain and enhance their competencies.
Training and Education Requirements
EMS training programs vary in length and intensity depending on the level of certification sought. Basic Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) training typically involves 120-150 hours of classroom instruction and hands-on experience, covering topics such as patient assessment, airway management, and basic life support.
Advanced EMTs receive additional training in more advanced medical procedures, such as intravenous therapy and medication administration. Paramedics undergo the most extensive training, including advanced medical techniques and critical care management.
Importance of Ongoing Professional Development
The field of emergency medical services is constantly evolving, with new technologies and treatments emerging regularly. EMS personnel must engage in ongoing professional development to stay abreast of these advancements. This includes attending continuing education courses, participating in simulations, and reading professional journals.
Levels of EMS Certification
There are three primary levels of EMS certification:
- Emergency Medical Responder (EMR):EMRs provide basic first aid and emergency care, such as CPR and bleeding control.
- Emergency Medical Technician (EMT):EMTs are trained to provide more advanced medical care, including airway management, oxygen administration, and splinting.
- Paramedic:Paramedics are the most highly trained EMS professionals, capable of providing critical care interventions such as intubation, medication administration, and cardiac monitoring.
EMS Technology
Technology plays a crucial role in modern Emergency Medical Services (EMS). It enhances communication, improves patient care, and streamlines operations, enabling EMS professionals to respond to emergencies more efficiently and effectively.
One of the most significant advancements in EMS technology is the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS). GPS devices allow EMS providers to locate patients quickly and accurately, even in remote or unfamiliar areas. This technology has significantly reduced response times and improved patient outcomes.
Communication Devices
Reliable communication is essential for EMS operations. EMS providers rely on a variety of communication devices, including radios, cell phones, and satellite phones, to stay connected with dispatchers, hospitals, and other emergency responders. These devices allow EMS crews to receive and transmit patient information, coordinate resources, and request assistance when needed.
Medical Monitoring Equipment
Medical monitoring equipment is used by EMS providers to assess and monitor patients’ vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This equipment helps EMS professionals make informed decisions about patient care and transport. Advanced medical monitoring devices, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) machines and defibrillators, allow EMS providers to provide life-saving interventions in the field.
Emerging Technologies
The future of EMS is shaped by emerging technologies that promise to further enhance patient care and improve operational efficiency. These technologies include:
- Telemedicine:Telemedicine allows EMS providers to consult with physicians and other healthcare professionals remotely, enabling them to receive expert advice and make informed decisions about patient care.
- Drones:Drones can be used to deliver medical supplies to remote areas, transport patients to hospitals, and provide aerial surveillance during emergencies.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI-powered systems can assist EMS providers with patient assessment, triage, and treatment recommendations, freeing up time for more critical tasks.
EMS Quality Improvement
EMS quality improvement is essential for ensuring that patients receive the best possible care. By continuously measuring and improving performance, EMS providers can ensure that they are providing safe, effective, and efficient care.There are a number of different methods that can be used to measure and improve EMS performance.
These include:
Data collection
Collecting data on patient outcomes, process measures, and other indicators can help EMS providers identify areas where they can improve.
Performance improvement
Using data to develop and implement interventions that are designed to improve performance.
Feedback
Providing feedback to EMS providers on their performance can help them identify areas where they need to improve.
Data Analysis and Feedback
Data analysis and feedback are essential components of quality improvement efforts. By analyzing data, EMS providers can identify trends and patterns that can help them understand how they can improve performance. Feedback can help EMS providers understand how their performance is perceived by patients and other stakeholders.By using data analysis and feedback, EMS providers can make informed decisions about how to improve performance.
This can lead to better patient outcomes, improved efficiency, and reduced costs.
EMS Special Operations
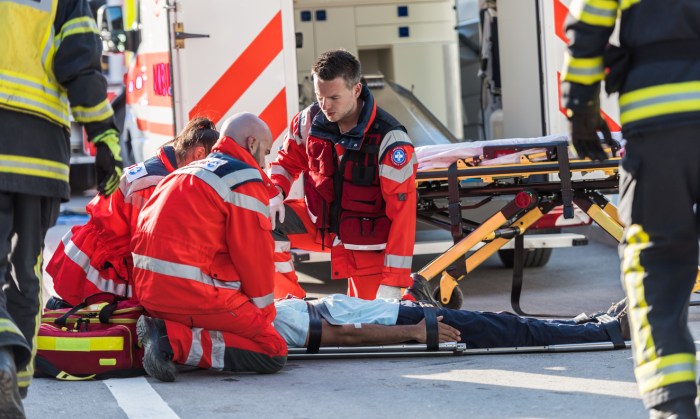

EMS plays a crucial role in special operations, including mass casualty incidents, disaster response, and tactical medicine. These operations present unique challenges, requiring specialized training and equipment.
Mass Casualty Incidents
EMS teams must rapidly mobilize and triage large numbers of casualties in mass casualty incidents. They prioritize treatment and transportation based on the severity of injuries, ensuring efficient and effective care.
Disaster Response
EMS provides medical support during natural disasters, such as hurricanes and earthquakes. They establish field hospitals, coordinate evacuations, and provide long-term medical care in affected areas.
Tactical Medicine, Emergency medical services
Tactical EMS supports military and law enforcement operations. They provide immediate medical care in hostile environments, including combat zones and active shooter situations.
Closing Summary: Emergency Medical Services
Emergency medical services are essential to modern healthcare, providing life-saving interventions and ensuring the well-being of our communities. As technology continues to advance and medical knowledge expands, the role of EMS will continue to evolve, ensuring that those in need receive the best possible care in their most critical moments.
Detailed FAQs
What are the different levels of EMS certification?
EMS certification levels vary depending on the region and country. Common levels include Emergency Medical Responder (EMR), Emergency Medical Technician (EMT), Paramedic, and Critical Care Paramedic.
What is the role of technology in EMS?
Technology plays a vital role in EMS, from GPS navigation and communication devices to medical monitoring equipment. Emerging technologies, such as telemedicine and artificial intelligence, are also shaping the future of EMS.
What are the challenges faced by EMS personnel?
EMS personnel face a range of challenges, including long working hours, exposure to traumatic events, and the need to make quick decisions in high-stress situations.





Leave a Comment